Dental implants are surgically implanting a pure titanium metal into the alveolar bone of the missing teeth area. After one to three months, a crown is placed on the artificial root. In addition to withstanding normal chewing force, dental implants almost have the same function and aesthetics as real teeth. Therefore, dental implants have been recognized by the stomatology community as the first choice to restore missing teeth.
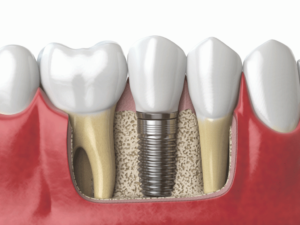
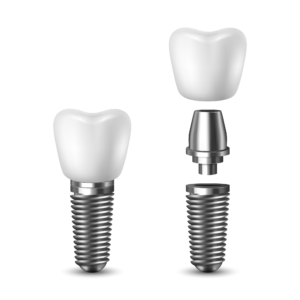
The standard procedures for dental implant include thorough examination, implant surgery and supra-implant restoration. A detailed examination should be performed at the beginning, which include intra-oral examination, extra-oral examination, X-ray examination, and CT (Computerised Tomography) scan to determine the position for dental implants. Then the dental implant surgery is performed under local anaesthesia. A standard dental implant surgery protocol included the following steps: raise a gum flap, drill a hole into the jawbone at the pre-determined position, insert the dental implant and suture the gum flap. After 3-6 months, the dental implant should unite with the jawbone. Then a second stage surgery might be performed to shape the gum around the dental implants. When the gum heals up, dental impressions will be taken for supra-implant restorations. The restorations (crown, bridge or denture) are fabricated in the dental laboratory and fixed onto the dental implants.
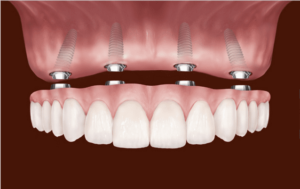
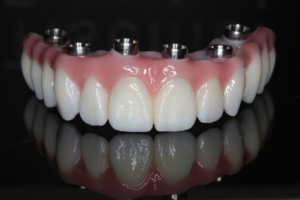
Apart from the conventional dental implant procedures, there are some other dental implant methods, such as immediate implant. In suitable cases, immediate implant could be performed, which means a dental implant surgery is performed immediately after dental extraction. The advantages for immediate implant include shorten treatment time and better aesthetics.
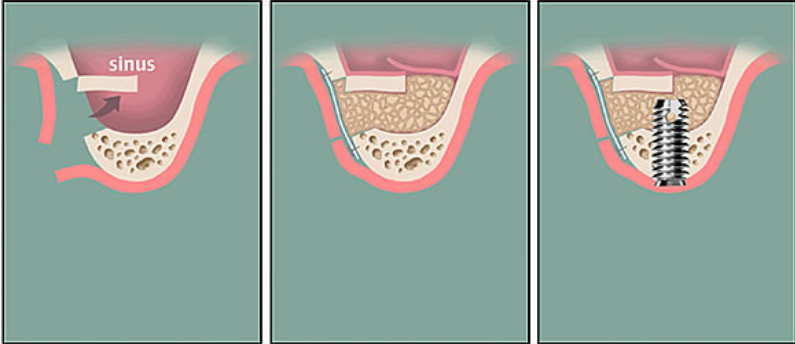
In some cases, the jawbone conditions may not be good enough to support dental implants. Then the jawbone volume could be increased through guided bone regeneration, sinus lift and so on.

